Placenta Previa & Cerebral Palsy
There are a number of pregnancy complications that can cause cerebral palsy. Some of these birth injuries are simply accidental while others are the result of a medical error either during pregnancy, delivery, or after childbirth. Placenta previa is a complication of pregnancy that can lead to cerebral palsy if left untreated.
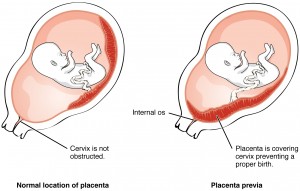
Placenta previa is a complication in which the placenta rests on the pregnant woman’s cervix. This unnatural placental placement can cause significant bleeding or hemorrhaging before and during the delivery process. A woman will usually notice the first warning signs of the condition late in the second trimester or in the third trimester of pregnancy with the appearance of bright red vaginal bleeding. This is usually a warning to most pregnant women to consult with their obstetricians or go to the emergency room.
The woman may also experience pre-term contractions or cramping/pain in the vaginal area. Anytime there is bleeding during pregnancy, you should consult with a medical professional right away. If the bleeding is caused by placenta previa, it can become severe enough to threaten the life of both the mother and her unborn baby.
The Role of the Placenta in Pregnancy
The placenta is a sac that is filled with amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus in the uterus, where it provides the unborn baby with oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products from its bloodstream. In a normal pregnancy, the placenta attaches to the upper section of the uterine wall, but during placenta previa it attaches to the lower section of the uterine wall which causes a partial or full blockage of the cervical opening. The biggest problem placenta previa presents is severe bleeding before, during, and after childbirth which endangers the lives of the mother and the unborn baby.
Risk Factors
Some of the risk factors for the development of placenta previa during the process of childbirth include the following:
- Mother is past the age of 35
- Mother previously underwent a uterine rupture or surgical procedure to the uterus
- The uterus is irregularly shaped
- Previous pregnancies or multiple births
- Smoking or substance abuse before or during pregnancy
- Pregnancy was the result of in vitro fertilization
Treatment of Placenta Previa
When an expectant mother is diagnosed with placenta previa, the doctor will probably order her to discontinue any physical activity for the rest of the pregnancy. In addition, the development of complications will probably result in an emergency cesarean section. There are a number of treatment recommendations the doctor might make prior to delivery, but it will depend of several factors including why the mother has developed placenta previa. While the doctor may weigh the risks of earlier delivery vs. allowing bleeding to continue, when the pregnancy is beyond 36 weeks, delivery is preferred; usually by cesarean section.
Monitoring by the doctor is essential in order to ensure a safe delivery for mother and baby. If the doctor detects placental previa yet fails in his/her duty to mitigate the harm to your child, they open themselves up to the possibility of a medical malpractice lawsuit.
